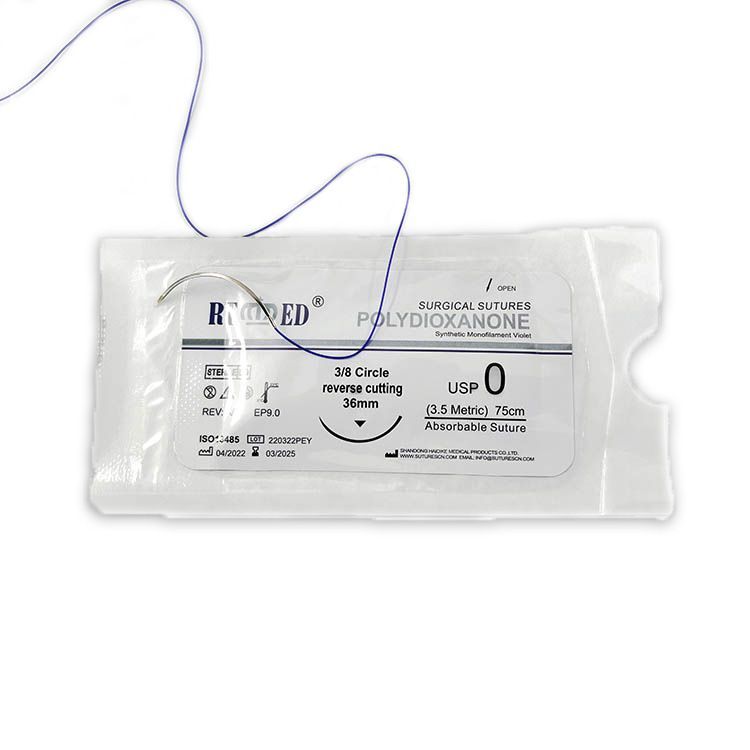
Suture Absorbable en PDO (Polydioxanone)
Polydioxanone (PDO) is a sterile, absorbable, synthetic monofilament suture composed of polyester polydioxanone. PDO absorbable suture has been proven to be non-antigenic and non-pyrogenic.
There are two main characteristics of absorbable PDO sutures, namely tensile strength retention and secondly, absorption rate. Absorbable PDO suture is available dyed purple in sizes ranging from USP 9/0 to USP 2.
Features :
- Compliance with the requirements of the European Pharmacopoeia (EP).
- Reduced incidence of infections and trauma due to its smooth surface.
- Smooth tissue passage.
- Predictable loss and higher strength compared to Catgut.
Indications :
PDO sutures are generally preferred when the combination of an absorbable suture and longer wound support is desired. PDO is commonly used in general surgery, including pediatric surgery, ophthalmic surgery, gastrointestinal surgery, gynecology, plastic surgery, urology, and orthopedics.
They are not used for adult cardiovascular tissues, neurology and prosthetic devices.
Properties :
Results of in vitro studies on PDO suture indicate that 70% of its initial strength persists after 4 weeks and 50% of its initial strength persists after 6 weeks.
Complete absorption of the PDO suture takes 6 to 7 months.
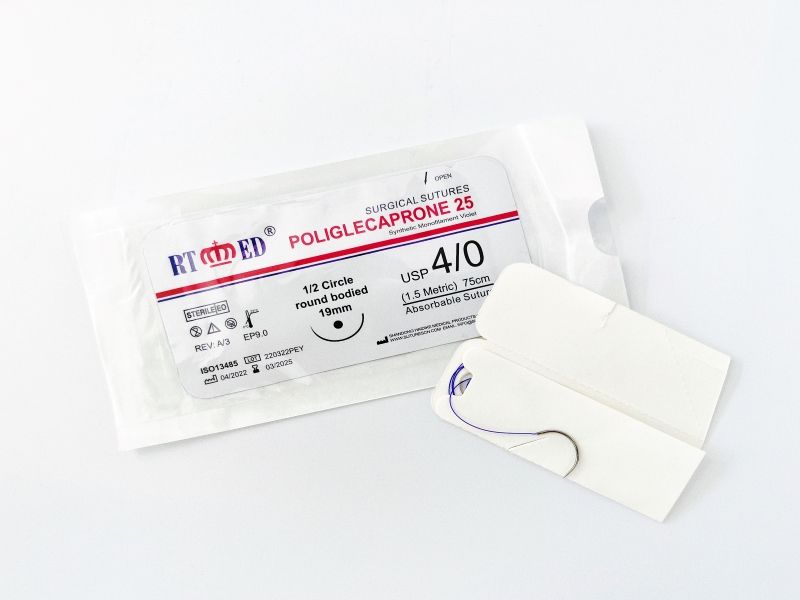
Suture Absorbable en PGCL (Polyglycolide-Co-Caprolactone)
Poliglecaprone 25 Absorbable Suture (PGCL) is a sterile synthetic monofilament suture composed of a copolymer of polyglycolide and caprolactone. PGCL absorbable suture is available dyed and undyed. The undyed suture is tan in color. PGCL suture is available dyed purple in the following sizes: USP 5/0 to USP 2.
Benefits :
- High initial tensile strength.
- Manipulation facile.
- Smooth passage through tissues.
- Excellent knotting ability.
Indications :
PGCL sutures are indicated for use in general surgery. They are suitable for soft tissue covering and ligation, particularly in plastic, gynecological, gastrointestinal, and urological surgery. PGCL sutures are absorbable and should be used when medium-term wound support is required. They are not intended for use in cardiovascular and neurological tissues.
Properties :
PGCL sutures retain 60% of their tensile strength by the first week and 30% by the second week. Hydrolysis degradation then begins, where the copolymer breaks down into glycolic acid, which is absorbed by the body between 90 and 110 days.
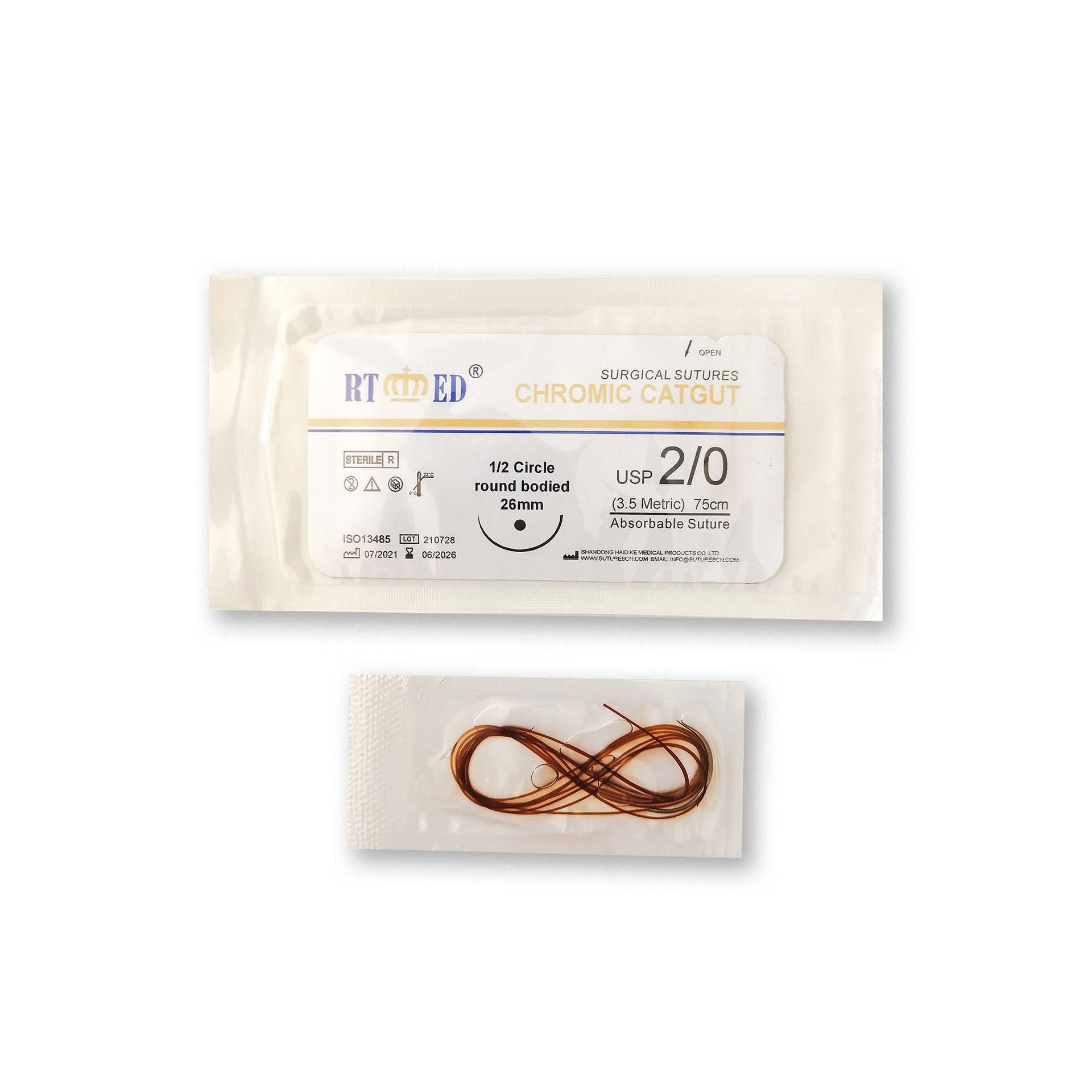
Chromic catgut sutures
Catgut surgical suture (natural and chrome) is a sterile absorbable surgical suture composed of purified connective tissue (primarily collagen) derived from either the serous layer of the ox (bovine) or the submucosal fibrous layer of the sheep (ovine) intestine.
Chrome Catgut is treated with a solution of glycerin and chromic salt to delay absorption.
- Features :
- Catgut sutures are naturally absorbable.
- Chrome catgut sutures are treated with chromic salt and have a dark brown color.
- Chrome catgut sutures are available in sizes USP 4 to 7-0.
- Catgut sutures are made by longitudinally slitting the intestinal submucosa of sheep and goats, followed by a twisting and polishing process, giving the sutures a virtually monofilament finish.
- Chrome catgut sutures are absorbed by a simple enzymatic hydrolytic mechanism, and absorption is not as predictable as in synthetic sutures. Catgut sutures tend to be absorbed more rapidly in infected tissue.
- Chrome catgut sutures retain approximately 50% of the initial tensile strength after 21 to 28 days of implantation, and the suture is essentially absorbed within 90 days.
- Benefits :
- Chrome catgut sutures pass through tissues smoothly and also have good knot security.
- Chrome catgut sutures have excellent tensile strength and resistance to needle attachment.
- Chrome catgut sutures are available with 300 series alloy steel needles for superior strength, sharpness and performance.
- Chrome catgut is available at very economical prices.

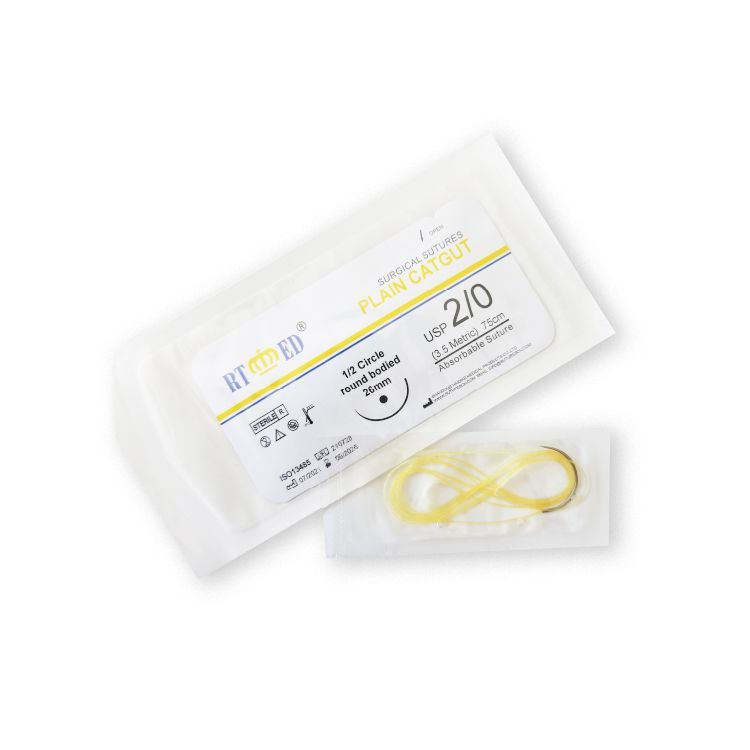
Catgut sutures
Single catgut suture is a sterile, absorbable, monofilament suture. The color of single catgut surgical suture is yellow, and the size ranges from USP 7/0 to 4.
Simple catgut is made from connective tissue (mainly collagen) from the serous layer of cattle or the submucosal fibrous layer of sheep intestine. Simple catgut is packaged with a solution containing isopropanol, water, sodium benzoate, and diethylaminoethanol. Sterilized by gamma rays. Its validity is five years.
Product Profile:
- Color: Yellow
- Composition: Purified connective tissue
- Size: USP 7/0 - USP 4
- Absorption type: Proteolysis
- Sterilization: Gamma radiation
- Absorption: 60 to 70 days
Suture Absorbable en PGLA (Polyglycolide-Co-Lactide)
Description :
Polyglactin (PGLA) is a sterile, absorbable, multifilament synthetic suture composed of polyglactin 910 glycoside and lactide derived from glycolic and lactic acids. It is coated with a blend of caprolactone/glycolide copolymer and calcium stearoyl lactylate.
PGLA sutures are available in purple and undyed color in sizes ranging from USP 8/0 to USP 2.
PGLA sutures are coated with polycaprolactone and calcium stearate.
Features :
- High tensile strength.
- Excellent handling and tying characteristics.
- Smooth passage through tissues.
- Easy to tie and fasten.
- Excellent knot security.
- Reliable absorption.
Indications :
Absorbable PGLA sutures are indicated for use in general surgery. They are suitable for soft tissue covering and ligation, including ophthalmic procedures, but should not be used on cardiovascular and nervous tissue. They are also applicable in gynecology, pediatric surgery, gastrointestinal surgery, and dentistry. PGLA sutures are absorbable and should not be used when long-term suture support is required.
Properties :
Absorbable PGLA sutures retain 70% of their tensile strength by the first week and 50% by the third week. Hydrolysis then begins, where the polymer breaks down into glycolic acid, which is fully absorbed by the body between 56 and 70 days.
Sterilization:
Ethylene oxide.
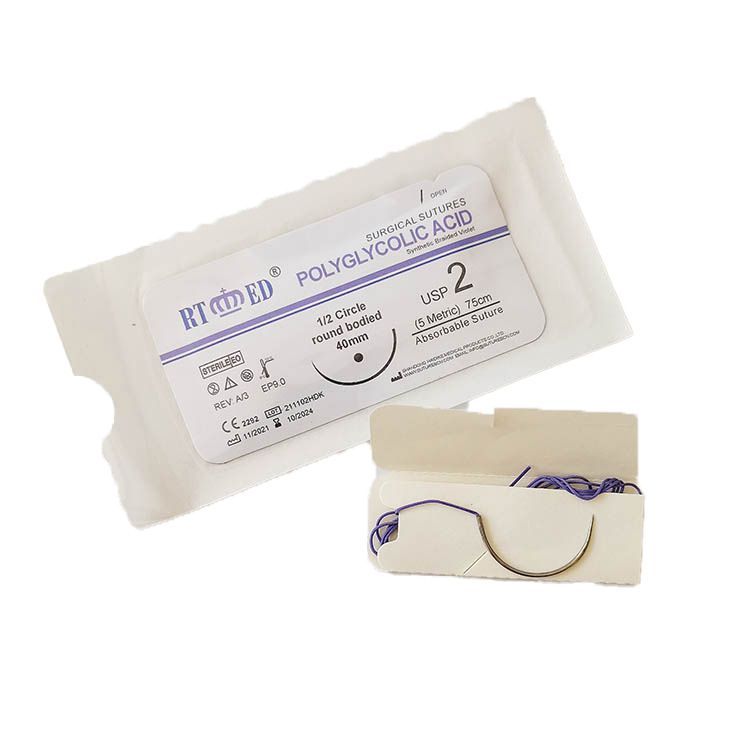
PGA suture threads
Polyglycolic acid (PGA) is a sterile, absorbable, multifilament synthetic suture composed of glycolic acid. The sutures are braided and coated with a blend of polycaprolate, a copolymer of caprolactone and glycolide, and calcium stearate.
The color of PGA absorbable suture is purple or undyed. The size ranges from USP 8/0 to USP 4.
Features :
Absorbable suture is widely used in surgery because it can be absorbed, thus avoiding the need for suture removal and avoiding secondary pain. PAG absorbable suture has the following obvious characteristics:
- High initial tensile strength
- Excellent knotting ability
- Exceptional support during the critical wound period
- Reliable absorption
- Easy to handle
- Secure knot retention
- Smooth surface, glides smoothly through fabrics
Indications :
Absorbable PGA sutures are indicated for use in general surgery. They are suitable for covering soft tissues, ligation, and also for use in ophthalmic procedures, but are not suitable for use in cardiovascular and nervous tissues. They are also applicable in gynecology, pediatric surgery, gastrointestinal surgery, and dentistry. Surgical PGA sutures are absorbable and are not suitable for areas requiring suture support for an excessively long period.
Properties :
Absorbable PGA sutures have a high initial strength that is maintained for up to 28 days. They retain 70% of their tensile strength at the 2nd week and 50% at the 3rd week. Then, absorption by hydrolysis begins, where the polymer degrades into glycolic acid, which is fully absorbed by the body between 60 and 90 days.
Sterilization:
Ethylene oxide.



